If you’ve been pitched on SEO a million times or have had a bad experience with an SEO agency, you may be feeling like you should just do SEO yourself.
While that feeling is certainly understandable, it’s unlikely you’ll be able to master all of the tactics and tricks a seasoned SEO consultant has learned after many years of practice in a short period of time. Especially if you’re in a competitive niche.
It’s also worth pointing out, that if you’re an owner or CEO of a brand or business, you should be working “on” your business a bit more than you are “in” it. And if you run your own marketing agency, that might mean you should consider working with a white label SEO partner.
Now that you’ve been warned of the obstacles ahead, let’s dive in.
Can you do SEO by yourself?
The short answer is YES.
Could you go to law school and become a lawyer? Sure.
Could you run for President?
While it’s certainly possible to do SEO yourself, SEO consultants have years of experience and plenty of battle scars that will give them insights into the correct SEO strategy for your brand.
And when you think about it, since big wins from SEO often take 6 to 12 months to take hold, SEO experts need years of experience to really become an expert. It takes a lot of time to get reps in the SEO field so you can understand what works and what doesn’t. And most importantly, to fix what is broken.
But, with that being said, you can do SEO yourself, and here’s how.
How to do SEO by Yourself in 2023
If you really want to do SEO yourself, you’re going to need to learn about all of the following topics:
1) Technical SEO
2) Keyword Research
3) Content Writing
4) On-Page Optimization
6) SEO Tools
7) How to track Performance
8) How to understand results
Technical SEO Basics You Need to Master:
Technical SEO is one of the harder aspects of SEO to master. Mainly because it requires some backend understanding of how websites and servers work. While you won’t need to become a programmer to dip your toes into technical SEO, you should have an understanding of the items below.
Indexability & Crawlability
Indexability and crawlability refer to if Google and other search engines can actually crawl your website and index your web pages so they can be found online. If your web pages can’t be crawled and aren’t indexed, your prospective customers are going to find your competitors instead of you.
Site Speed
Site speed is becoming more and more important in the SEO space. This is because more and more people are using their phones to search, so much so that Google actually indexes websites mobile-first.
From a user experience perspective, imagine waiting 5 or 10 seconds for a website to load. Most people don’t have that kind of patience and will head back to Google to find a website that will load faster.
Mobile-Friendliness
As mentioned a minute ago, more and more people are searching on their mobile phones, which means it’s essential to make your website mobile-friendly. Being mobile-friendly extends beyond site speed, as you want the experience of viewing and navigating your website to be seamless as well.
Duplicate Content
You’re probably familiar with plagiarism, and duplicate content is a close cousin. While having duplicate content doesn’t mean you’ve plagiarized content from another website, it does mean you’ve used the same content on your own website on multiple pages.
Google wants unique and helpful content for users, and reusing the same content across multiple web pages goes against that concept. You need to avoid duplicate content at all costs.
XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a file you can submit to Google Search Console that tells Google which pages you want Google to crawl. Sitemap files are often organized by page type, meaning their will be a section for collections, blog posts, products, and any other page types you want to include.
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is when you tell Google to send users to a different page than the one they typed into their browser. This is useful when you’ve changed domains, URLs, or removed pieces of content from your website.
404s and other response codes
Similar to 301 redirects are 404s and other server response codes. A 404 error is when someone tries to access a page on your website and that page doesn’t exist. Ideally, you want people to find what they are looking for, so resolving 404 errors and other server response codes can be a great way to keep people on your website and get them to the content they are looking for.
Structured Data
Structured data is a powerful and often underutilized part of SEO. You can markup your website code to share information about product reviews and other valuable data to Google. If you’ve ever noticed some ecommerce products on Google that have their star-rating showing, this is because they have properly implemented structured data to show those ratings.
Finding Broken Links
A broken link is a link that links to a page that does not exist. These create a subpar user experience and make life difficult for Google when they are crawling your website. It’s important to clean these up as you find them.
Using Canonical Tags
A canonical tag is a meta tag that you can add to your web pages that tells Google which page it should actually index when there are pages that are similar on a website. A good example of this is when an ecommerce product has product variants.
Product variants often produce multiple URLs for a single product. Instead of indexing all of the variants and multiple URLs for this one product, you can use a canonical tag to tell Google which URL you want to be indexed out of those variants.
Keyword Research: More than just picking random words out of a hat
When I talk with people that don’t do SEO, there is this misconception that you just throw keywords onto a page or do keyword stuffing to help pages rank. While keyword stuffing was a strategy 15+ years ago, it’s not a strategy that will get you very far today.
Instead, when doing keyword research you need to understand some of the following.
Searcher Intent
Searcher intent is understanding what someone wants to find when typing a specific phrase into Google. If they just want information, you should provide content that is informative. If they are ready to buy, you want to get a collection or product page ranking for that keyword. The overall idea is to give people what they are looking for.
Top, Middle & Bottom Funnel Searches
Depending on what stage of the buyer’s journey they are on, a searcher is going to be looking for different types of content. This is where viewing your content in terms of top of the funnel, middle of the funnel, and bottom of the funnel can be helpful.
At the top, someone might have a question or a piece of information they need. In the middle, they might start comparing different products or brands or features. And then at the bottom, they are ready to buy and need content that will convince them to spend their money.
Keyword Difficulty
Keyword difficulty is a rather straightforward concept. How difficult is a keyword to rank for. This can be a helpful metric to understand in your keyword research as you might waste your time trying to rank for the most difficult keywords in your niche when there are low-hanging fruits to go after.
Primary Keywords vs Secondary Keywords
A primary keyword is a core topic you’re looking to rank for and the keyword you want a given page to rank number one for. A secondary keyword is a supporting topic or related idea that a given page can also rank for. The power of secondary keywords is that by using them in your content, you can show additional expertise on a subject and give a page the opportunity to rank for more than just the primary keyword.
Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization is similar to duplicate content that was mentioned in the technical SEO portion of this post. Cannibalization is when multiple pages are trying to rank for the same keyword. This is a big no-no in SEO as it will confuse Google and make it hard for Google to decide which page it should rank for that keyword, which usually winds up negatively affecting all of those pages.
SEO Content: A Different Beast Than Writing an Article
While you shouldn’t write content directly for Google, writing content that will rank on Google is still a different task than writing an article that might wind up in a magazine or newspaper.
Here are some things you’ll need to understand to create quality SEO content.
How to write for users & Google
This is the hardest thing to master for most writers. Balancing writing for users and Google. While Google will often reward content that users find helpful, you need to rank in the first place for people to find the content. With you’re writing approach, you need to understand what is already ranking, plus what new approach or angle you can add to your content to make it stand out.
Leveraging Headings
Headings are gold when it comes to SEO writing. Heading can be a great place to add in secondary keywords and using them properly will also make your posts easier to skim, meaning readers will find what they need easier. Making a post easier to read keeps people on the page longer, which Google likes to see.
How to use secondary keywords
As mentioned a few times in this post, secondary keywords are essential to have SEO success. In addition to using secondary keywords in your headings, they can be a great way to answer multiple questions your customers have in one post, which will position you as more authoritative than other brands and businesses.
How to organize content for readability
Making your content readable is one of the best ways to keep people reading your content. When someone is searching on their phone or computer, they are usually not interested in reading huge chunks of content like they might when reading a novel.
Instead, it’s helpful to break content up into shorter paragraphs and to use headings to organize your content.
It’s also helpful to keep the reading level of your content lower than you might expect. You don’t need to write for a college audience, and in most cases, you shouldn’t. This is because the average person reads at a middle school reading level. So, keep it simple.
How to make unique content
Some SEO experts take the approach of just writing the same article that is already ranking. That doesn’t always work out that well. While you should consider what has helped those articles rank, you also need to come up with a unique angle that adds value not seen in other blogs currently ranking for that keyword.
How to turn readers into buyers
Lastly, when it comes to SEO content, you need to write content that actually converts website visitors into buyers! This means understanding how to leverage features and benefits of products and services in your content to convince people to buy.
On-Page Optimization: Taking Care of the Basics
When people say they are going to “do SEO themselves” they often wind up taking care of the basics of on-page SEO optimization. While the basics can help, there are some advanced on-page strategies most people ignore.
Writing a proper meta title
A meta title is what shows up in blue text on Google search results. This needs to include your primary keyword and also convince people to click and visit your website.
Writing meta descriptions
The meta description also shows up on Google and is the sentence you see below the meta description. This can also be used to help sell a searcher on visiting your website and is a great opportunity to position your product or service as the correct choice.
Image alt text and optimization
Images are a huge part of on-page SEO, as Google image search is a popular place for people to shop for products. By properly tagging your images with alt text, you’ll increase the likelihood of those images showing up on Google and earning you organic traffic.
Additionally, optimizing those images to load fast can help with site speed, which will positively affect the user experience and rankings of your website as well.
Internal linking
Internal linking is one of the most underutilized SEO tactics. Similar to backlinks, internal links can connect ideas and topics across your website and help send authority from one page to another.
Proper HTML structure
How you structure your web pages is a key part of SEO as well. Using headings, and lists, and having a site that uses responsive web design will make your website perform well on Google searches.
URL slugs
A URL slug is less disgusting than it sounds. In fact, they should be short and easy to read. A slug is the text that comes after the forward slash in a URL and should include your primary keyword when possible.
Proper External Linking
We’ve already discussed internal links, but there are also external links, which are links that point to other websites. While it’s not a requirement to have external links, when you do, you want to make sure that these links open in a new window so users stay on your website longer.
Building Backlinks: Getting Authority to Your Website
A lot of people get scared when backlinks come up. They are either afraid of them because they believe they are “black hat” or just don’t know how to build them. The truth is, backlinks are one of the most important ranking signals.
Just think about it, if no other websites link to your website, how will Google or other users find you?
You simply need links. There are many websites out there that do an amazing job at creating content and handling technical and on-page SEO but still don’t rank simply because they don’t build backlinks.
To successfully build links, you’ll need to learn:
How to do link outreach
Link outreach is when you email other websites and ask them to add a link to your website. There is a wide range of strategies for reaching out, but at the end of the day, you need to provide something of value in this exchange to make it work.
How to prospect quality websites for link placements
While getting links is important, you need to prospect for the right websites to build them from. Getting links from sites with inflated domain ratings or low-quality content won’t help you as much as getting links from other websites with existing authority and rankings.
Proper Anchor Text Usage
Anchor text is the text that your backlink comes from. Overoptimizing your anchor text for a specific keyword can actually negatively affect your rankings. You need to have a balanced approach with the anchor text you use to avoid penalties from Google and to actually positively influence rankings.
Where you should point your links
It’s also important to point your links to the right pages on your website. A lot of links wind up getting built to the homepage, but it’s also important to send link authority to other pages as well.
Topical Relevance
A lot of link builders focus on domain authority (we’ll get to that in a second), and while that is something to consider in your link building efforts, I’ve found topical relevance to be even more important.
Topical relevance means getting links from content that actually talks about what you sell or about something related to what your website discusses. This shows Google that other people covering the same topics as your website care enough to link to you as well.
Domain Authority
Domain Authority or Domain Rating are not metrics made by Google, but rather metrics developed by Ahrefs and MOZ, two of the larger software companies in the SEO space.
Both of these metrics work on a scale of 0 to 100 and the higher you go up the scale, the harder it is to climb. You can expect websites like the New York Times or Wall Street Journal to have ratings in the 90s, so it’s important to set your authority goals relative to your niche.
When it comes to getting backlinks, getting links from more authoritative websites can give your site more authority, as long as that website hasn’t tried to inflate or manipulate that metric, which is possible and happens more often than you think.
How many links do you need to compete
It’s also important to understand how many links you’ll need to compete with your competitors. If there is a massive gap or you’re in a competitive space, you’ll need to have more link velocity than if you were in an easier-to-rank niche.
SEO Tools: Using the Right Tool for the Job
There’s a phrase I use often when discussing SEO tools, and that is, “use the tool, but don’t let the tool use you.” That’s because it can be easy to get caught up in the different metrics SEO tools provide.
Some people hyperfocus on Domain Rating or their content score in SurferSEO, when really they need to consistently take action on SEO strategies that move the needle. Mainly, building more links, creating more content, and staying on top of technical issues.
The truth is, there’s always more you can do in SEO. These tools can help get you organized and make your SEO process more efficient.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is a keyword research tool and is a favorite amongst some of the best SEOs in the world. In addition to keyword research and rankings, Ahrefs has tools to analyze backlinks, research existing content, and compare your website to competitors.
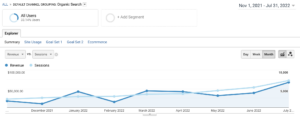
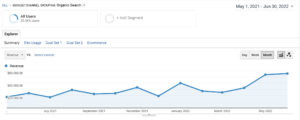
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free tool that helps you track your website traffic and conversions. While there is a ton of data you can pull from analytics, one of the most important ones is understanding which marketing channels are performing.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is another tool that is free and super powerful. It can help with submitting new pages to be crawled by Google, and for seeing how many impressions and clicks you are getting for specific keywords and understanding which keywords your getting those impressions and clicks from.
Google search console is a great tool for finding new keyword phrases that aren’t yet showing up in Ahrefs or other research tools and for finding underperforming pages that could use an update.
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is a more technical tool, but super powerful. It allows you to crawl any website as if you were Google or another bot and pull down data from every web page on your website. You can also connect Screaming Frog to other tools, like Ahrefs and Google Search Console, to make extremely data-oriented SEO decisions.
SurferSEO
Funnily enough, I’m writing this article in SurferSEO! SurferSEO is a powerful tool that can help you optimize content ideas and gives you recommendations on word count and which keyword phrases you should use throughout your content.
It’s important to keep in mind, that you still need to write unique content and using SurferSEO incorrectly is an easy way to overoptimize your content.
SEOTesting
SEOTesting is another one of my favorite tools. It allows you to set up tests with your content. One of my favorites to run is doing a click-thru-rate test after changing a meta title and description of a page on a client’s website.
SEOTesting connects to Google Search Console and will pull in data for what you are testing for a given time period. Once the testing period has been completed, the tool will let you know which version had the most impressions and clicks.
Website platforms like WordPress & Shopify
When doing SEO, you’ll also wind up using different website platforms. Not surprisingly, different platforms require different approaches to SEO as each platform has its strengths and weaknesses.
Various Plugins
While you don’t want to use too many plugins (the extra javascript can slow your website down), you’ll also need to master a wide range of plugins, like Yoast SEO, to properly optimize your website.
Tracking SEO Performance
You can do all the SEO you want, but if you aren’t tracking your performance, you’ll have no clue if you’ve made progress or have started trending in the wrong direction.
To properly track SEO, you need to:
Gather baseline metrics for rankings, backlinks, traffic, & sales
Make sure Google Analytics & Google Search Console are set up properly
Setup Ahrefs or another tracking tool properly
In addition to tracking SEO performance, you also need to be able to understand results.
This is especially important early on in a campaign.
If you’re unable to analyze data in Ahrefs, Google Search Console, & Google Analytics you’ll be in the dark during your SEO campaign.
Does Doing SEO Yourself Sound like a lot of Work? Hire Noah Kain Consulting Instead
If you’ve gotten through this post and still feel confident about your ability to do SEO yourself, more power to you. If you’re feeling overwhelmed and ready to work with an agency that has a proven track record and process, reach out to our team at Noah Kain Consulting today to schedule a call.